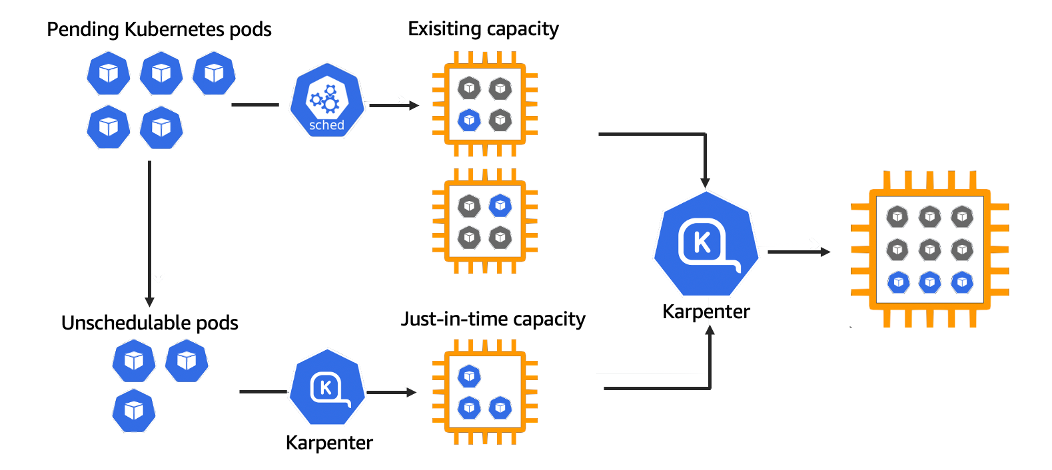
Karpenter是一个AWS提供的节点生命周期管理器,它会观察传入的pod并根据情况启动正确的节点。节点选择决策基于策略并由传入的pod的规范驱动,包括资源请求和调度约束。
它的主要作用:
- 为不可调度的Pod启动节点
- 替换现有的节点提高资源利用率
- 如果超时或者不需要,则终止节点
- 在抢占前优雅终止节点
优点
Karpenter观察未调度的Pod的聚合资源请求,并做出启动和终止节点的决定,以最大限度地减少调度延迟和基础设施成本。
优势
- 更快:Karpenter在AWS上直接与EC2队列API通信,可以根据pod的规格直接选择正确的实例类型,以实现快速自动扩展
- 更省钱:Karpenter根据工作负载要求提供节点,可以将pod打包成最小数量的适当大小节点,并节省成本
- 更灵活:使用karpenter无需创建数十个节点即可实现灵活性和多样性
- 对比原生的Cluster-Autoscaler,规避其原生的一些缺陷:例如在集群中添加或删除的容量限制、不能在Auto Scaling组中使用混合大小的集群…
- Karpenter自动检测存储依赖,例如如果原来节点拉取在A区,Pod第一次拉起时有创建PV(Persistent Volume),后续节点启动决策时会自动创建在A区(因为EBS是单可用区的,如果手动创建跨AZ可能会导致访问不通)
使用方法
前置准备
- 需要部署Metrics Server, 采集pod和node的指标用于资源约束
- 安装Karpenter controller, 这是Karpenter的核心控制器
- 安装Karpenter dashboard, 用于查看Karpenter管理的节点以及性能指标
karpenter provisioner 的模板
1 | apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5 |
同时需要配置node template 模板
1 | apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5 |
原理
利用Karpenter的分层约束模型,pod运行受到三层约束
- 需要在依赖的应用程序或存储可用的区域中运行
- 需要特定种类的处理器或者硬件(需要有对应的Node)
- 希望使用拓扑扩展等技术来确保高可用性
第一层由云服务器厂商对硬件的类型,区域进行限制;第三层由其他技术控制pod调度;Karpenter通过设置Provisioner对指定节点进行调度和决策,从而满足第二层的控制
通过Provisioner 可以做到的限制包括
- 资源请求:请求一定数量的内存或CPU。
- 节点选择:选择在具有特定标签(nodeSelector)的节点上运行。
- 节点亲缘性: 绘制pod以在具有特定属性(亲缘性)的节点上运行。
- 拓扑扩展: 使用拓扑扩展来确保应用程序的可用性。
Pod亲和性/反亲和性: 根据其他Pod的调度将Pod引向或远离拓扑域。
Karpenter 控制节点上下线的方式包括以下几种,
- 删除Provisioner:删除Provisioner就会优雅下线其所有的节点
- Emptiness: 当节点上不存在非daemonset的工作负载,同时启动了ttlSecondsAfterEmpty时,会在时间结束后回收节点
- Expiration: 当设置了ttlSecondsUntilExpired 后,节点到达过期时间就会自动下线
- Consolidation: Karpenter基于积极的节约策略,主动删除或者将节点换成更便宜的节点
- 具体策略:
- 如果一个节点的所有pod都可以在集群中其他节点的空闲容量上运行,则可以删除节点。
- 如果一个节点的所有pod都可以在集群中其他节点的空闲容量和一个更便宜的替换节点的组合上运行,那么它就可以被替换。
- Interruption: 启动中断检测后karpenter会判断节点是否即将发生中断事件并主动下线节点
Drift:karpenter会下线出现漂移的节点,同时也会主动检测,把实例上使用的AMI与AWSNodeTemplate设置的AMI不匹配的节点打上标记 - 手动删除: 通过eksctl 主动删除节点,同样会被karpenter优雅下线处理
使用场景
在aws中可以代替固定节点组的创建,基于taint以及 亲和性反亲和性,指定更灵活的策略进行节点的调度与约束